Prepaid vs. credit cards sets the stage for understanding the nuances of these financial tools, guiding readers through a journey of comparison and contrast to make informed decisions.
Explore the key differences between prepaid and credit cards, their functionalities, and the pros and cons associated with each, empowering you to navigate the realm of personal finance with confidence.
Overview of Prepaid and Credit Cards
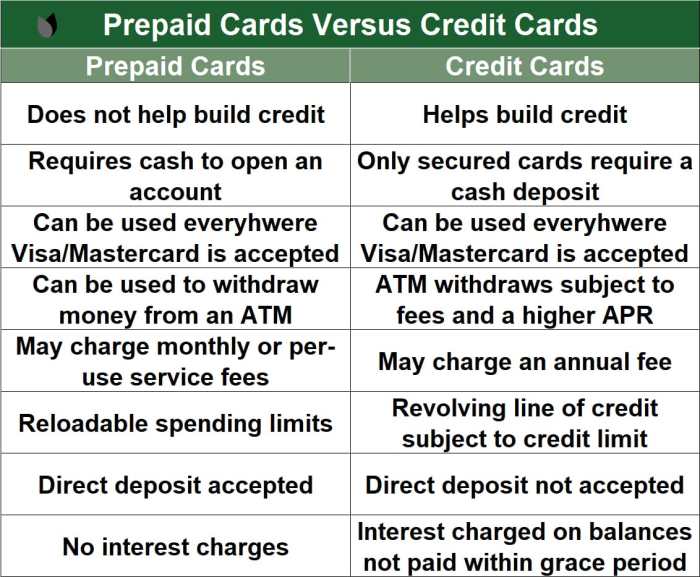
Prepaid and credit cards are two popular financial tools that individuals use for making purchases, but they operate quite differently. Prepaid cards are loaded with a specific amount of money that can be spent until the balance is depleted, while credit cards allow users to borrow money up to a certain limit and pay it back later.
Main Features of Prepaid Cards
Prepaid cards are not linked to a bank account and do not require a credit check for approval. Users can only spend the amount loaded onto the card, making it a useful budgeting tool. These cards can be reloaded with additional funds as needed and are widely accepted for purchases.
Main Features of Credit Cards
Credit cards are issued by financial institutions and allow users to borrow money up to a predetermined credit limit. Users are required to pay back the borrowed amount, usually with interest, within a specified period. Credit cards offer rewards, cashback, and other benefits based on usage.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Prepaid and Credit Cards
- Advantages of Prepaid Cards:
- Helps with budgeting and controlling spending.
- No risk of accumulating debt since users can only spend what is loaded.
- Accepted at most merchants that accept credit cards.
- Disadvantages of Prepaid Cards:
- May have fees for activation, reloading, or inactivity.
- No credit-building opportunities since transactions are not reported to credit bureaus.
- Limited in terms of protection against fraud or unauthorized charges.
- Advantages of Credit Cards:
- Convenient for making purchases online and in-store.
- Opportunity to earn rewards, cashback, or travel points.
- Builds credit history and improves credit score with responsible use.
- Disadvantages of Credit Cards:
- High-interest rates if balances are not paid in full each month.
- Potential to accumulate debt beyond means to repay.
- Risk of damaging credit score with late payments or high credit utilization.
How Prepaid Cards Work
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/what-difference-between-prepaid-credit-card-and-gift-card_round2-fb12f0c05cc04888832041224c23a9a3.png?w=700)
Prepaid cards work by allowing users to load funds onto the card in advance, similar to a gift card. These cards are not linked to a bank account and can be used until the balance runs out.
Loading Funds onto a Prepaid Card
Prepaid cards can be loaded with funds by transferring money from a bank account, depositing cash at a participating retailer, or receiving direct deposits. Once the funds are loaded onto the card, it can be used for purchases just like a debit or credit card.
Reloading a Prepaid Card
Reloading a prepaid card can be done by visiting a retailer or financial institution that supports the specific card, transferring funds from a bank account, or setting up direct deposits. Some cards may also offer the option to reload funds online or through a mobile app for added convenience.
Benefits of Using a Prepaid Card
– Budgeting: Prepaid cards can help users stick to a budget as they can only spend the amount loaded onto the card.
– Security: Since prepaid cards are not linked to a bank account, users are not at risk of exposing sensitive financial information.
– Travel: Prepaid cards are convenient for travel as they can be used internationally and offer currency conversion options without foreign transaction fees.
How Credit Cards Work
Credit cards function as a convenient financial tool that allows users to borrow money from the card issuer up to a predetermined credit limit. This borrowed amount must be repaid within a specified period, usually on a monthly basis.
Importance of Making Timely Payments
Making timely payments on a credit card is crucial to maintaining a good credit score. Late payments can result in penalties, increased interest rates, and negatively impact your credit history. By paying off the full balance or at least the minimum amount due each month, cardholders can avoid these consequences and build a positive credit profile.
Potential Risks of Using a Credit Card
- Accumulating Debt: One of the main risks associated with credit cards is the temptation to overspend and accumulate debt that may become difficult to repay.
- High Interest Rates: Credit cards often come with high-interest rates, especially for unpaid balances, which can lead to significant financial burdens if not managed responsibly.
- Identity Theft and Fraud: Using credit cards online or in unfamiliar places can expose cardholders to the risk of identity theft and fraudulent transactions, potentially causing financial losses and damage to credit scores.
- Credit Score Impact: Mismanaging a credit card by missing payments or exceeding the credit limit can negatively impact your credit score, making it harder to access loans or other financial products in the future.
Acceptance and Usage: Prepaid Vs. Credit Cards

Prepaid and credit cards differ in terms of acceptance and usage, impacting where and how they can be used. While both can be convenient payment methods, there are distinctions to consider.
Acceptance Comparison, Prepaid vs. credit cards
- Prepaid cards: Prepaid cards are generally not as widely accepted as credit cards. They may not be accepted for certain transactions like car rentals or hotel bookings, where a credit card is required for security purposes.
- Credit cards: Credit cards are widely accepted worldwide and are the preferred payment method for many online and in-person transactions.
Common Usage
- Prepaid cards: Prepaid cards are commonly used for budgeting purposes, travel, online shopping, and as gifts. They are a convenient way to control spending and manage finances.
- Credit cards: Credit cards are commonly used for everyday purchases, travel bookings, dining out, and emergencies. They offer rewards, cashback, and travel benefits that can enhance the overall user experience.
Tips for Maximizing Benefits
- Prepaid cards: Load only the amount you plan to spend to avoid overspending. Look for prepaid cards with low fees and features like ATM access and rewards programs to maximize benefits.
- Credit cards: Pay off the full balance each month to avoid interest charges. Take advantage of rewards programs, cashback offers, and travel perks to maximize the benefits of using a credit card.
Closure
In conclusion, weighing the benefits and drawbacks of prepaid vs. credit cards equips individuals with the knowledge to select the optimal payment method that aligns with their financial goals and lifestyle. Make wise choices and leverage these financial instruments to enhance your monetary management strategies.
When it comes to managing finances as a student, having a credit card can be a useful tool. However, choosing the right one can be overwhelming for beginners. That’s why exploring the options for student credit cards for beginners is crucial.
These cards often come with lower credit limits and tailored benefits that cater to students’ needs, making them a great starting point for building credit history responsibly.
When it comes to managing finances as a student, having a credit card can be a useful tool. However, choosing the right one can be overwhelming for beginners. That’s why exploring options like student credit cards for beginners is crucial.
These cards often come with lower credit limits and fewer fees, making them ideal for those new to credit. Additionally, they can help build a positive credit history if used responsibly.